|
Volcanoes are mountains which are connected to the molten rock in the center of the earth. There are three types of volcanoes: cinder cone, shield, and composite cone. Each kind of volcano forms in a slightly different way but each one can erupt with amazing force.
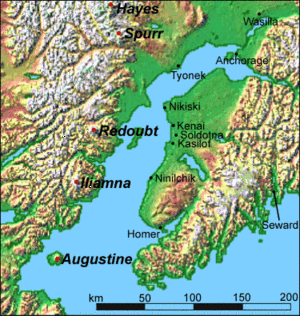
There are several volcanoes through out Alaska's National Parks. Lake Clark contains Iliamna and Redoubt volcanoes. Mount Redoubt, or Redoubt Volcano, is an active stratovolcano in the largely volcanic Aleutian Range of the state of Alaska. Located in the Chigmit Mountains, part of the Aleutians, the mountain is just west of Cook Inlet, in the Kenai Peninsula Borough.
Built above the Aleutian subduction zone over the last 890,000 years, Redoubt is now heavily glaciated and boasts an ice-filled summit crater. Mount Redoubt towers 9,000 feet (2,700 m) above the surrounding valleys to the north, south, and southeast in little over 5 miles (8 km); it is also the third highest within the range, with nearby Mount Torbert, at 11,413 feet, being the highest and Mount Spurr at 11,070 feet being the second highest.
It is potentially one of the most dangerous volcanoes in Alaska. Redoubt has erupted explosively at least five times since Captain James Cook observed the volcano steaming in 1778. The eruptions have all originated from a vent at the north end of the summit crater. The oldest historical eruption occurred in 1902, when explosions were heard hundreds of kilometers away and extensive ashfall blanketed the Cook Inlet area. Explosive eruptions in the 1960s caused flooding and lahars from melting glaciers, and created ash plumes that reached 6 km in height. Mount Redoubt has erupted five times since 1900: in 1902, 1922, 1966, 1989 and 2009.. Alaska's Redoubt Volcano blew on Dec. 15, 1989, and sent ash 150 miles away into the path of a KLM jet carrying 231 passengers. Its four engines flamed out. The jet dropped more than 2 miles, from 27,900 feet to 13,300 feet, before the crew was able to restart all engines and land the plane safely at Anchorage.
Redoubt has recently shown signs that it may be entering a new period of activity, including increased seismicity and active summit degassing. Renewed activity would pose a major risk to air traffic in the region around the volcano, and ash from an eruption could reach as far as the continental US.
From the most recent eruption of Redoubt, scientists identified certain types of rocks within the magma, finding the magma is made up of a lot of silica. Magma chockfull of silica is viscous and traps lots of gases. Only when that magma gets to the surface, where pressure decreases, can that gas exit, similar to opening up a shaken soda. With those types of magmas you can get a very stiff rock foam rising to the surface, and the only way the gases can eventually come out when they encounter lower pressure is to literally blow the foam apart,. Magma from the Hawaiian volcanoes like Mount Kilauea is typically basaltic, which contains much less silica and is much less viscous. That means gases can percolate out of the magma much easier, leading to calmer eruptions. Redoubt is not the only volcano which threatens aircraft and creates ash-related hazards. Areas where explosive volcanic eruptions are common, such as the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, the islands of Indonesia and the Philippines, and the highlands of Central and South America, are constantly being monitored in order to prevent disastrous interaction between aircraft and volcanic clouds.
|